Παραμετρικοί τύποι
Παράδειγμα: ζευγάρι
class Pair <E1, E2> {
private final E1 element1;
private final E2 element2;
public Pair(final E1 e1, final E2 e2) {
element1 = e1;
element2 = e2;
}
public E1 getFirst() {
return element1;
}
public E2 getSecond() {
return element2;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + element1.toString() + ", " + element2.toString() + ")";
}
}
class Sock {}
class Man {}
class Woman {}
class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Pair <Sock, Sock> pairOfSocks;
Pair <Man, Woman> churchMarriedCouple;
Pair <Man, Man> civilPartners;
}
}
Παραμετρικοί τύποι στη Java
-
Στη Java ορίζουμε παραμετρικούς τύπους με το όνομα μιας
κλάσης ή διεπαφής ακολουθούμενο από μια λίστα από ορίσματα.
Pair <Sock, Sock>
Pair <Man, Woman>
Vector <String>
Collection <Integer>
Collection <Pair <Sock, Sock>>
- Με βάση τους παραμετρικούς τύπους ορίζουμε
γενικεύσεις (generic) κλάσεων και μεθόδων.
- Παράμετρος ενός τύπου επιτρέπεται να είναι κάποιος
τύπος αναφοράς (reference type)
(κλάση, διεπαφή, ή πίνακας) ή ένας τύπος μπαλαντέρ (wildcard).
Παραμετρικοί τύποι μπαλαντέρ
Παράδειγμα γενίκευσης
class LinkedList <E> {
/** Node's value */
private E value;
/** Next node */
private LinkedList <E> next;
/** Construct a list with a single element v */
LinkedList(final E v) {
value = v;
next = null;
}
/** Return a list with element n added to it */
public LinkedList <E> add(final E v) {
var n = new LinkedList <E>(v);
n.next = this;
return n;
}
/** Return a string representation of the list */
@Override
public String toString() {
final String me = value.toString();
/* Recursive implementation */
if (next == null)
return me;
else
return me + " -> " + next;
}
/** Test harness */
static public void main(String args[]) {
var ilst = new LinkedList <Integer>(0);
ilst = ilst.add(1);
ilst = ilst.add(18);
ilst = ilst.add(45);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
ilst = ilst.add(i * 10);
System.out.println(ilst);
}
}
Παράδειγμα υπερφόρτωσης μεθόδων
double
square(final double x)
{
return x * x;
}
Complex
square(final Complex x)
{
return new Complex(
square(x.real) + square(x.imaginary),
2 * x.real + x.imaginary);
}
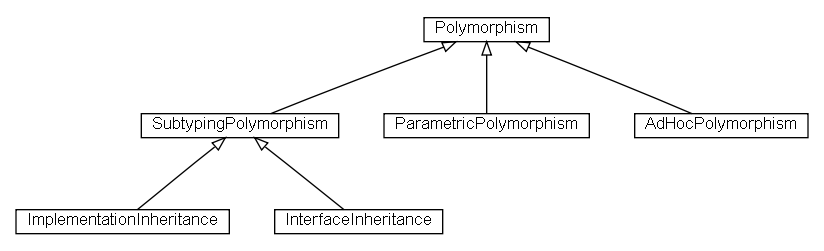
Ανακεφαλαίωση πολυμορφισμού
Έχουμε στο σημείο αυτό εξετάσει όλα τα είδη
πολυμορφισμού (polymorphism):
-
πολυμορφισμό υποτύπων (subtyping polymorphism)
μέσω:
-
κληρονομικότητας υλοποιήσεων (implementation inheritance)
(μηχανισμός extends) και
-
κληρονομικότητας διεπαφών (interface inheritance)
(μηχανισμός implements),
-
παραμετρικό πολυμορφισμό (parametric polymorphism)
(παραμετρικοί τύποι και γενικεύσεις), και
-
πολυμορφισμό ad-hoc
(υπερφόρτωση μεθόδων και
switch με ταίριασμα προτύπων).
Χρήση πολυμορφισμού
Σε συνηθισμένες εφαρμογές σχεδιάζουμε συχνά με κληρονομικότητα
διεπαφών, ενώ συναντάμε:
- σε έτοιμες κλάσεις (π.χ. για γραφικές διεπαφές) κληρονομικότητα υλοποιήσεων και
- σε έτοιμα πλαίσια συλλογών παραμετρικό πολυμορφισμό.
Διάγραμμα πολυμορφισμού
Νήματα
- Ένα νήμα (thread) παριστάνει μια ροή εκτέλεσης του
προγράμματος.
- Ένα πρόγραμμα μπορεί να εκτελεί πολλά νήματα ταυτόχρονα.
- Με τον τρόπο αυτό μπορούμε
- να υλοποιήσουμε εφαρμογές που απαιτούν ταυτόχρονη
ή ψευδοταυτόχρονη πολλαπλή επεξεργασία
(π.χ. εξυπηρετητές (servers) ή παιγνίδια)
- να ελαττώσουμε το χρόνο που περιμένει ο χρήστης για την
ολοκλήρωση μιας διεργασίας
- να εκμεταλλευτούμε καλύτερα τους πόρους πολλαπλών επεξεργαστών
Αδιέξοδο

Νήματα: προβλήματα
Όταν υλοποιούμε κώδικα με νήματα δημιουργούνται συχνά προβλήματα
συγχρονισμού που πρέπει να αντιμετωπίσουμε.
- Διαφορετικά νήματα μπορούν να έχουν πρόσβαση στην
ίδια μεταβλητή ή πόρο του συστήματος με τρόπο που να δημιουργεί λάθη.
- Στην προσπάθεια να λύσουμε το παραπάνω πρόβλημα κλειδώνοντας
την εκτέλεση κάποιων νημάτων μπορεί να καταλήξουμε σε
αδιέξοδο (deadlock)
Τα στοιχεία αυτά δεν καλύπτονται στο συγκεκριμένο μάθημα.
Νήματα: εναλλακτικές
Αντί για νήματα μπορούμε συχνά να χρησιμοποιήσουμε
- πολλαπλές διεργασίες π.χ. Apache httpd
- γεγονότα (events) π.χ. Windows API
- ασύγχρονες (asynchronous) διεπαφές π.χ. node.js
- ροές (streams) δεδομένων π.χ. φλοιός Unix
Ορισμός νήματος στη Java
- Στη Java κάθε νήμα παριστάνεται ως ένα αντικείμενο μιας κλάσης
που υλοποιεί τη διεπαφή Runnable.
- Η διεπαφή Runnable απαιτεί την υλοποίηση μιας και μόνο μεθόδου
public void run()
- Η μέθοδος run περιέχει τον κώδικα που εκτελεί το νήμα.
- Μέσα στη μέθοδο run πρέπει να αντιμετωπίσουμε την εξαίρεση
InterruptedException ή οποία μπορεί να συμβεί αν ένα άλλο νήμα
τερματίσει τη λειτουργία μας.
Χρήση νήματος στη Java
Παράδειγμα χρήσης νημάτων
public class CocktailGuest implements Runnable {
/** What the guest will say */
private final String mumble;
/** How many seconds will he/she pause before speaking */
private final int pause;
/** How long the guest will stay */
private final int stay;
/** How long the guest has stayed */
private int hereFor;
/** Constructor */
public CocktailGuest(String mumble, int pause, int stay) {
this.mumble = mumble;
this.pause = pause;
this.stay = stay;
hereFor = 0;
}
/** Execution method */
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (hereFor < stay) {
Thread.sleep(pause * 1000);
hereFor += pause;
System.out.println(mumble);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Something has come up; got to go.");
return;
} finally {
System.out.println("Good bye.");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
final int NGUEST = 5;
var guest = new CocktailGuest[NGUEST];
var thread = new Thread[NGUEST];
int i = 0;
guest[i++] = new CocktailGuest("Can I have another drink?", 8, 30);
guest[i++] = new CocktailGuest("Nice food!", 7, 120);
guest[i++] = new CocktailGuest("Ha ha ha...", 3, 100);
guest[i++] = new CocktailGuest("Hi, I am Maria.", 5, 60);
guest[i++] = new CocktailGuest("Hello, I am Petros.", 15, 60);
// Create the threads
for (i = 0; i < NGUEST; i++)
thread[i] = new Thread(guest[i]);
// Start the threads
for (i = 0; i < NGUEST; i++)
thread[i].start();
}
}
Άσκηση: χρήση παραμετρικών τύπων και νήματα
Άσκηση 12
Μπορείτε να κατεβάσετε το αντίστοιχο αρχείο και να στείλετε τους
βαθμούς σας από τους δεσμούς που βρίσκονται στη
σελίδα των ασκήσεων.
Βιβλιογραφία
- Rogers CadenheadΠλήρες εγχειρίδιο της Java 12Όγδοη έκδοση. Εκδόσεις Μ. Γκιούρδας, Αθήνα 2023. Κεφ. 7.
- Herbert Schildt. Οδηγός της Java 7. 5η έκδοση. Εκδόσεις Γκιούρδας Μ., Αθήνα 2012. Κεφ. 11, 13.
- Harvey M. Deitel και Paul J. Deitel. Java Προγραμματισμός, 6η έκδοση. Εκδόσεις Μ. Γκιούρδας, Αθήνα 2005. Κεφάλαιo 23.
- Else Lervik και Vegard B. Havdal Java με UML. Εκδόσεις Κλειδάριθμος 2005. Κεφάλαιο 16.
- Γιώργος Λιακέας
Εισαγωγή στην Java. σ. 153, 172-173 371-412,
Εκδόσεις Κλειδάριθμος 2001.
- Γιάννη Κάβουρα. Προγραμματισμός με Java. Εκδόσεις Κλειθάριθμος, Αθήνα 2003. σ. 328, 355-366, 485-492
- Rogers Cadenhead και Laura Lemay Πλήρες εγχειρίδιο της Java 2 Εκδόσεις Μ. Γκιούρδας, Αθήνα 2003. σ. 141-167, 179-208.
- Herbert Schildt Herb Schild's Java έτοιμες συνταγές Εκδόσεις Μ. Γκιούρδας, Αθήνα 2009. κεφ. 7
- K. N. King.
Java Programming: from the Beginning, pages 61–62, 300–305,
418–420, 465–466, 493–494.
W. W. Norton & Company, New York, NY, USA, 2000.
- Bo Sandén.
Coping with Java threads.
Computer, 37(4):20–27, April 2004.
Περιεχόμενα

